Epitaxial lateral overgrowth on the air void embedded SiO2 mask for InGaN light-emitting diodes
Abstract
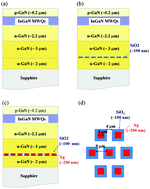
We fabricated InxGa1−xN multiple quantum well (MQW) light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on an air void embedded SiO2 mask using a simple process (silver (Ag) deposition, SiO2 capping, and high-temperature

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...