Inhibition of solution crystal growth of ritonavir by cellulose polymers – factors influencing polymer effectiveness†
Abstract
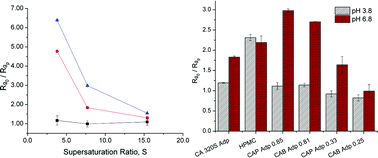
Inhibition of crystallization, either nucleation or crystal growth, from supersaturated solutions used to enhance the delivery of poorly water soluble drugs is an important area of study. The use of polymers as crystallization inhibitors may significantly impact the extent and duration of supersaturation and thus bioavailability. In this study, we investigate the principal factors influencing crystal growth inhibition of ritonavir by cellulose adipate polymers. Bulk crystal growth rates of ritonavir in the presence and absence of pre-dissolved polymer were estimated from seeded-desupersaturation experiments under different conditions of pH and supersaturation. It was found that the effectiveness of the cellulose adipate polymers decreased at low pH due to the pH-dependent ionization ratio of the adipate carboxyl group of these cellulose esters, which may influence the conformation and extent of coverage. The Kubota-Mullin model was used to predict the magnitude of growth inhibition. Above a critical supersaturation, the Kubota-Mullin model was quantitatively inaccurate, due to a change in growth mechanism from layer-face growth to fast continuous growth. The polymers were less effective at inhibiting crystal growth at the high supersaturation generated by the amorphous solid due to a fast continuous growth mechanism at high supersaturations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...