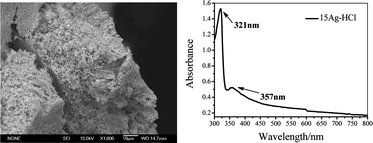
The dealloying processes of Al-Ag alloy ribbons consisting of two distinct phases of α-Al (Ag) and Ag2Al in the 5 wt.% H2SO4, 10 wt.% H3PO4, 10 wt.% C2H2O4 and 5 wt.% HCl solutions were investigated. The as-dealloyed samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis coupled with SEM. It has been found that the resultant microstructure of the as-dealloyed samples is significantly influenced by the initial alloy composition and the acid kind. The four acid solutions are all able to leach out the Al from both the α-Al (Ag) and Ag2Al phases and the as-dealloyed samples exhibit the typical three dimensional (3D) bi-continuous nanoporous structure. The dealloying duration in four acid solutions ranges from 1.1 to 24 h, and the dealloying rates are influenced by acidity, acid concentration, and the diffusion coefficient (Ds) of Ag atoms which is affected by anions and interactions between anions and Al atoms. The specific surface area of the nanoporous silver (NPS) from the Al-15 at.% Ag alloy dealloyed in HCl was determined as 3.47 ± 0.08 m2 g−1 through N2 adsorption experiments and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis. The Uv-vis absorption spectrum indicates that surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of silver nanostructure exists on the NPS samples, implying the potential application of NPS in surfaced enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-active substrate, surface plasmon-based analytical devices, etc.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...