Supramolecular solids and time-resolved diffraction
Abstract
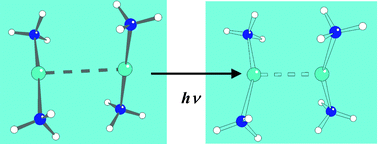
Supramolecular solids are an ideal medium for time-resolved diffraction studies at atomic resolution as they allow dilution of the active species, and the study of a species in different states of aggregation and different environments, but attention must be paid to excited-state quenching due to energy transfer. Crystallinity must be preserved up to reasonable product concentrations if chemical reactions are to be monitored at the atomic level.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...