Correlative imaging of ionic transport and electronic structure in nano Li0.5FePO4 electrodes†
Abstract
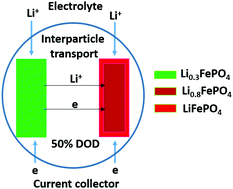
Phase separation and electronic structure variation of Li0.5FePO4, both in the bulk and surface, under concurrent lithiation, has been tracked by synchrotron X-ray microscopies. Oxygen K-edge XANES along with DFT calculations reveal unusual electronic structure varition which is attributable to the observed lithium gradient and interparticle transport. The new insights will benefit the future design of advanced batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...