Stiffness of cationized gelatin nanoparticles is a key factor determining RNAi efficiency in myeloid leukemia cells†
Abstract
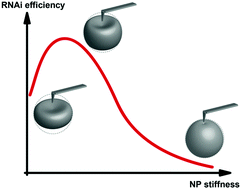
Here we demonstrated that the stiffness of cationized gelatin nanoparticles determined the efficiency of RNAi in myeloid leukemia cells when the particle size and surface charges were kept constant. The siRNA delivery system with an elastic modulus of 0.87 MPa showed the largest siRNA uptake and RNAi efficiency for hard-to-transfect suspension cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...