Methylations in complex carbapenem biosynthesis are catalyzed by a single cobalamin-dependent radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme†
Abstract
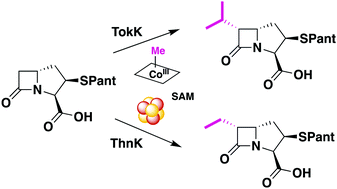
Complex carbapenem β-lactam antibiotics contain diverse C6 alkyl substituents constructed by cobalamin-dependent radical SAM enzymes. TokK installs the C6 isopropyl chain found in asparenomycin. Time-course analyses of TokK and its ortholog ThnK, which forms the C6 ethyl chain of thienamycin, indicate that catalysis occurs through a sequence of discrete, non-processive methyl transfers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...