Humid atmospheric pressure plasma jets exposed micro-defects on CoMoO4 nanosheets with enhanced OER performance†
Abstract
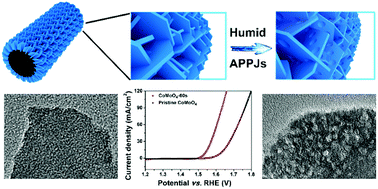
Humid atmospheric pressure plasma jets (APPJs) sustained in an argon/water vapour mixture were adopted to treat CoMoO4 nanosheets arrays, which resulted in micro-defects on the surface and the appearance of hydroxyl (OH−) groups absorbed on the nanosheets. Benefiting from these changes, the plasma treated CoMoO4 exhibited similar catalytic property to RuO2, an overpotential 70 mV lower than for pristine CoMoO4 and maintained good stability after 30 hours for the water oxidation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...