Programming a split G-quadruplex in a DNA nanocage and its microRNA imaging in live cells†
Abstract
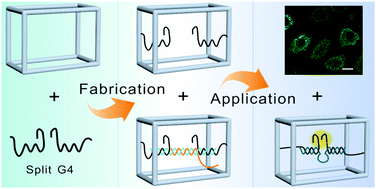
A novel approach to program target-responsive devices by incorporating the split G4 motifs in a DNA nanocage has been developed. The rigid prism outcompetes the flexible one in reaction kinetics and signal/background ratios, which can be easily internalized by cells and successfully applied in microRNA imaging in live cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...