A scalable electrochemical dehydrogenative cross-coupling of P(O)H compounds with RSH/ROH†
Abstract
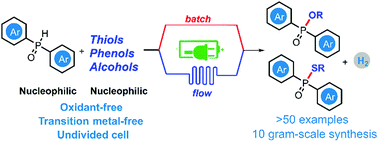
A practical, scalable electrochemical dehydrogenative cross-coupling of P(O)H compounds with thiols, phenols and alcohols in both an undivided cell and a continuous-flow setup is disclosed. Its broad substrate scope (>50 examples), good functional-group tolerance and scalability (>10 g) show potential for practical synthesis. A preliminary mechanistic study suggests that the phosphorus radicals are involved in the catalytic cycle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...