Remote control of electronic coupling – modification of excited-state electron-transfer rates in Ru(tpy)2-based donor–acceptor systems by remote ligand design†
Abstract
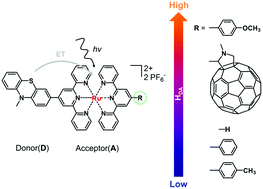
A comprehensive understanding of how the molecular structure influences the electronic coupling is crucial in optimizing (supra) molecular assemblies for photoinduced electron transfer. Here, we report that the electronic coupling underlying electron transfer from a phenothiazine donor to a photoexcited Ru(tpy)2 acceptor is modulated by substitution of the second (remote) tpy-ligand.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...