Diverse outcomes of CO2 fixation using alkali metal amides including formation of a heterobimetallic lithium–sodium carbamato-anhydride via lithium–sodium bis-hexamethyldisilazide†
Abstract
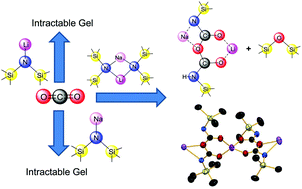
Fixation of CO2 by lithium amides derived from pyrrole and diisopropylamine generates a lithium carbamate polymer and dodecamer respectively. Moving to lithium–sodium hexamethyldisilazide produces a more complicated, intriguing reaction, where unusually the bimetallic composition is maintained in the product but its composition contains both carbamato and anhydride functionalities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...