Fluorescein sodium ligand-modified silicon nanoparticles produce ultrahigh fluorescence with robust pH- and photo-stability†
Abstract
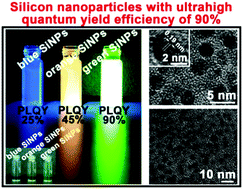
Water-dispersed silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) are facilely prepared in an aqueous phase via microwave-assisted synthesis. The whole synthetic procedure is accomplished in a one-pot microwave reaction, without the requirement of additional surface modification. Remarkably, the resultant SiNPs feature ultrahigh fluorescence (photoluminescent quantum yield (PLQY): ∼90%), robust pH- and photo-stability, and favourable biocompatibility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...