Nearly monodisperse PbS quantum dots for highly efficient solar cells: an in situ seeded ion exchange approach†
Abstract
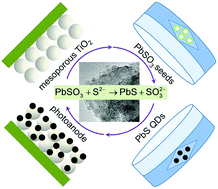
A facile in situ seeded ion exchange approach was used to produce nearly monodisperse and uniformly distributed PbS quantum dots (QDs) on mesoporous TiO2 films. This strategy solves the size distribution problem for conventional SILAR-processed QDs and shows promise for constructing high-performance near-infrared-responsive PbS QD solar cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...