Ruthenium nanoparticle catalyzed selective reductive amination of imine with aldehyde to access tertiary amines†
Abstract
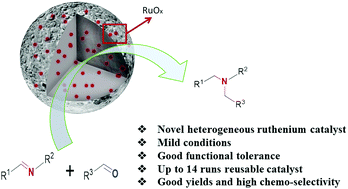
Reductive amination is one of the most frequently used transformations in organic synthesis. Herein, we developed a novel ruthenium nanoparticle embedded ordered mesoporous carbon catalyst (Ru–OMC) and a new hydrosilylation process for the synthesis of tertiary amines. We present a direct reductive amination of imines (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond) with aldehydes (C
N bond) with aldehydes (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond) using hydrosilane as the reducing reagent under mild conditions. Moreover, the Ru–OMC catalysts can be reused for up to 14 runs without noticeably losing activity.
O bond) using hydrosilane as the reducing reagent under mild conditions. Moreover, the Ru–OMC catalysts can be reused for up to 14 runs without noticeably losing activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...