ExciTides: NTP-derived probes for monitoring pyrophosphatase activity based on excimer-to-monomer transitions†
Abstract
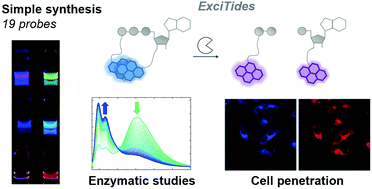
We describe a new type of nucleotide-derived fluorescent probe designed for monitoring pyrophosphatase activity based on excimer-to-monomer transitions, called ExciTide. The nucleotides were designed with two self-interacting dye moieties and synthesised using copper-catalysed azide–alkyne cycloaddition click chemistry. We applied these probes for enzyme activity monitoring and inhibitor evaluation. Some of the probes permeated into living cells, yielding interesting prospects for future applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...