Efficient hydrogen evolution from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane using bilateral-like WO3−x nanorods coupled with Ni2P nanoparticles†
Abstract
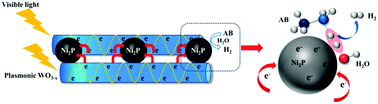
A ten times enhanced H2 evolution from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane was realized through bilateral-like plasmonic WO3−x nanorods coupled with Ni2P nanoparticles compared to Ni2P, which provides a new strategy to develop non-noble metal based plasmonic configurations for diverse energy and environment related applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...