Oxygen plasma treatment of HKUST-1 for porosity retention upon exposure to moisture†
Abstract
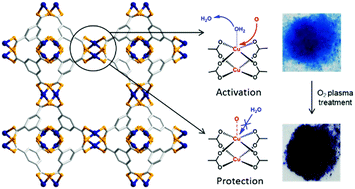
Despite their remarkable properties, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) present vulnerable structures that are sensitive to moisture; therefore, their application to real field situations is challenging. Herein, an O2 plasma technique was introduced as a new method for the activation and protection of porosity in HKUST-1. In an unprecedented manner, O2 plasma-treated HKUST-1 retains its porosity after a long exposure to moisture as compared to pristine HKUST-1. Porosity retention was examined by N2 adsorption/desorption measurements of non-activated HKUST-1 after exposure to moisture.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...