A phenazine-barbituric acid based colorimetric and ratiometric near-infrared fluorescent probe for sensitively differentiating biothiols and its application in TiO2 sensor devices†
Abstract
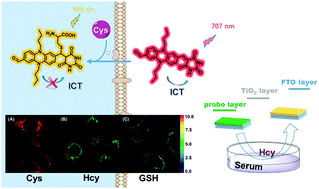
A new colorimetric and ratiometric near-infrared fluorescent probe based on phenazine-barbituric acid was developed to ultrasensitively detect biothiols. The favorable ratiometric changes helped the imaging and differentiation of Cys in living cells. Besides, the probe was successfully employed to construct TiO2 sensor devices, which could quantify Hcy concentration in serum.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...