Alloying barbituric and thiobarbituric acids: from solid solutions to a highly stable keto co-crystal form†
Abstract
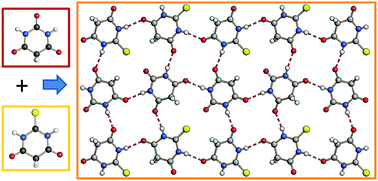
Alloying isomorphous crystals of barbituric acid (BA) and thiobarbituric acid (TBA) yields solid solutions of general formula BAxTBA1−x (x < 0.8); for x = 0.5 the stable co-crystal BA0.5TBA0.5, isomorphous with the parent keto forms, is observed, which melts at 265 °C, i.e. ca. 10 and 20 °C higher than the melting points of BA and TBA, respectively. While the BAxTBA1−x solid solutions with x > 0.5 are stable, those with x < 0.5 convert, with time or temperature, to the BA0.5TBA0.5 co-crystal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...