Silicon carbon nanoparticles-based chemiluminescence probe for hydroxyl radical in PM2.5†
Abstract
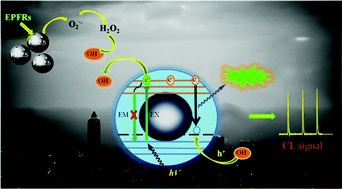
A new SiC nanoparticles (SiC NPs)-based chemiluminescence (CL) probe for selective and sensitive detecting of ˙OH has been developed. The radiative recombination of ˙OH-injected holes and electrons in the SiC NPs accounts for the CL phenomenon. Furthermore, the as-developed CL probe has been successfully applied to detect ˙OH in PM2.5.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...