Aluminothermic reduction enabled synthesis of silicon hollow microspheres from commercialized silica nanoparticles for superior lithium storage†
Abstract
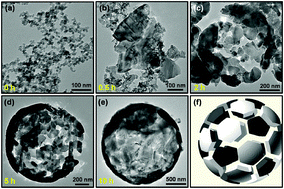
We report the aluminothermic reduction enabled synthesis of silicon hollow microspheres from commercialized silica nanoparticles by controlled transformation and organization. The synergistically integrated merits of a simple process and delicate structural design lay a basis for developing an industrially viable silicon anode with optimized electrochemical performances.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...