Modelling an electrochemically roughened porous platinum electrode for water oxidation†
Abstract
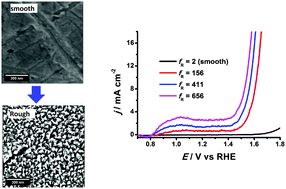
Pt is usually not considered as an efficient catalyst for water oxidation. Here, we report a design-of-experiment approach for modelling the roughness of an electrochemically roughened Pt electrode for water oxidation. The results indicate significant interaction between oxidation and reduction potentials on surface roughness and the porous Pt exhibits greatly improved catalytic activity for oxygen evolution in acid which is comparable to the benchmark catalyst RuO2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...