Nanoparticles self-assembled from multiple interactions: a novel near-infrared fluorescent sensor for the detection of serum albumin in human sera and turn-on live-cell imaging†
Abstract
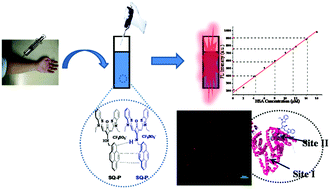
A novel pyrene-conjugated squaraine fluorescent probe SQ-P, which could self-assemble into nanoparticles in aqueous solution through multiple interactions, was designed to selectively detect serum albumin with a turn-on response in the near infrared (NIR) region. More importantly, the probe can quantitatively detect serum albumin in human sera, and be used for imaging in living cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...