Regioselective direct oxidative C–H cyanation of quinoline and its derivatives catalyzed by vanadium-containing heteropoly acids†
Abstract
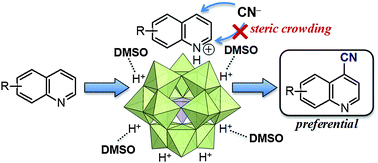
A direct oxidative C–H cyanation of quinoline and its derivatives using trimethylsilyl cyanide as the cyano source and molecular oxygen as the terminal oxidant has been developed. In the presence of catalytic amounts of vanadium-containing heteropoly acids, e.g., H7PV4Mo8O40, cyanation of various quinoline and its derivatives preferentially took place at the 4-position, affording the corresponding substituted 4-cyanoquinolines as the major products.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...