Assembly of bioactive multilayered nanocoatings on pancreatic islet cells: incorporation of α1-antitrypsin into the coatings†
Abstract
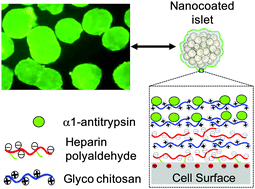
A spontaneous multilayer deposition approach for presenting therapeutic proteins onto pancreatic islet surfaces, using a heparin polyaldehyde and glycol chitosan alternating layering scheme, has been developed to enable the nanoscale engineering of a microenvironment for transplanted cells. The nanocoating incorporating α1-antitrypsin, an anti-inflammatory protein, exhibited effective anti-coagulant activities in vitro.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...