Reversible pH-controlled switching of an artificial antioxidant selenoenzyme based on pseudorotaxane formation and dissociation†
Abstract
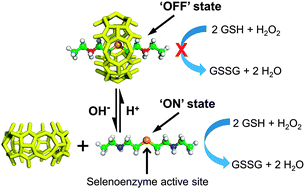
A pH-responsive artificial selenoenzyme was constructed by reversible binding between organoselenium compound 1 and CB[6] to form a pseudorotaxane-based molecular switch in response to pH stimuli. The glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity of the artificial selenoenzyme can be switched on/off in a mild and body suitable environment between pH = 7 and pH = 6.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...