Aggregates of silicon quantum dots as a drug carrier: selective intracellular drug release based on pH-responsive aggregation/dispersion†
Abstract
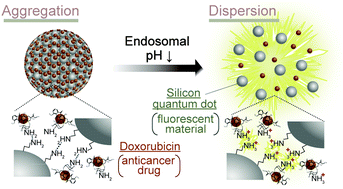
Using amine-modified silicon quantum dots (Si-QDs) with visible photoluminescence as a building block, drug-loaded Si-QD aggregates were assembled. The aggregates were designed to break down in response to the endosomal pH decrease, which enabled the selective intracellular release of the loaded drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...