Lewis acid-assisted detection of nerve agents in water†
Abstract
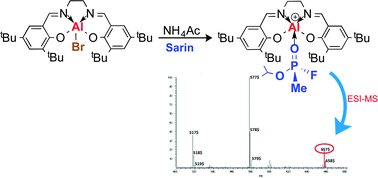
The five-coordinate compound, Salen(tBu)Al(Ac), prepared in situ from Salen(tBu)AlBr and NH4Ac, forms Lewis acid–base adducts in aqueous solution with the G-type nerve agents, Sarin and Soman, and the VX hydrolysis product, ethylmethylphosphonate (EMPA). The resulting compounds, [Salen(tBu)Al(NA)]+[Ac] − (with NA = Sarin, Soman, and EMPA) are sufficiently stable to be identified by ESI-MS. Molecular ion peaks were detected for every compound with little or no fragmentation. The distinctive MS signatures for the [Salen(tBu)Al(NA)]+ compounds provide a new technique for identifying nerve agents from aqueous solution. The energetics of the displacement of Ac− by the nerve agents to form [Salen(tBu)Al(NA)]+[Ac]− were determined computationally.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...