Surface enhanced vibrational spectroscopic evidence for an alternative DNA-independent redox activation of endonuclease III†
Abstract
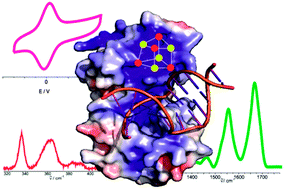
Surface enhanced vibrational spectro-electrochemistry of endonuclease III provides direct evidence that the [4Fe–4S] cluster is responsible for the enzyme redox activity, and that this process is not exclusively DNA-mediated, as currently proposed. We report the first surface enhanced resonance Raman spectrum of a [4Fe–4S]2+ cluster containing enzyme.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...