Electrochemically grown nanoporous MnO2 nanowalls on a porous carbon substrate with enhanced capacitance through faster ionic and electrical mobility†
Abstract
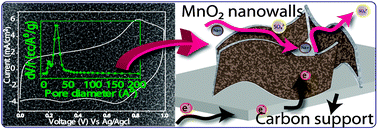
We report the deposition of uniform porous MnO2 nanowalls on a conducting carbon fiber substrate using a simple electrochemical method, which produces ordered nano-channels demarcated by the MnO2 walls for easy ion transport and a continuous electron path created by the carbon backbone. The system achieves a specific capacitance of 1149 F g−1 and retains 565 F g−1 even at dragging conditions as high as 100 A g−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...