Visible-light-driven water oxidation at a polychromium-oxo-electrodeposited TiO2 electrode as a new type of earth-abundant photoanode†
Abstract
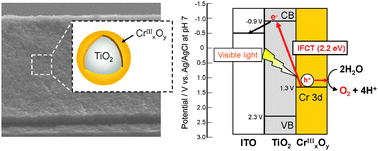
A polychromium-oxo-deposited TiO2 electrode was fabricated as an earth-abundant photoanode for visible-light-driven water oxidation by a simple electrochemical technique. The photoelectrocatalytic water oxidation could occur based on a specific interfacial charge transfer (IFCT) from a CrIII to the TiO2 conduction band.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...