Pinning effect for photoisomerization of a dicationic azobenzene derivative by anionic sites of the clay surface†
Abstract
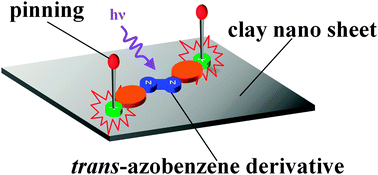
The photoisomerization behaviour of a dicationic azobenzene derivative on the inorganic surface was examined. The isomerization reaction was controlled by the charged array of the inorganic surface due to the “pinning effect” because of the electrostatic interaction between anionic charged sites on the inorganic surface and cationic charged sites in dye molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...