A mechanistic investigation of hydrodehalogenation using ESI-MS†
Abstract
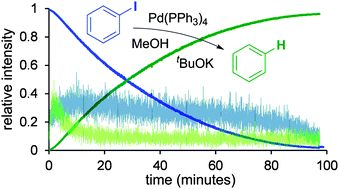
The rate of hydrodehalogenation of aryl iodides with a palladium catalyst in methanol exhibits a strong primary kinetic isotope effect from both CD3OD and CH3OD, suggesting that deprotonation plays a major role in the mechanism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...