Counter-cation modulation of hydrogen and methane storage in a sodalite-type porous metal–organic framework†
Abstract
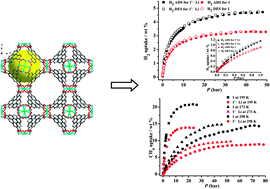
A μ4-Cl bridged anionic sodalite-type porous metal–organic framework (Et2NH2)3[(Cu4Cl)3(TTCA)8]·26DEF was synthesized, in which Et2NH2+ can be exchanged by Li+

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...