Control of electron-transfer reduction by protonation of zinc octabutoxyphthalocyanine assisted by intramolecular hydrogen bonding†
Abstract
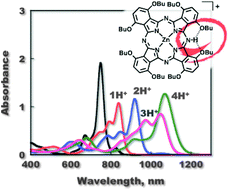
Facile protonation of α-octabutoxyphthalocyaninato zinc(II) (Zn(OBu)8Pc) occurs to afford up to tetra-protonated species stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding, resulting in positive shifts of the reduction potentials of Zn(OBu)8PcHnn+ (n = 1–4) with increasing the number of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...