High surface area ZnO–carbon composite tubular arrays based on the Kirkendall effect and in situZn evaporation†
Abstract
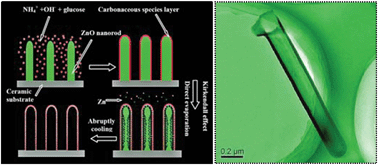
High surface area ZnO–carbon composite tubular arrays on a ceramic substrate were successfully synthesized by a hydrothermal process and a subsequent nanoscale diffusion-related reaction within the carbonaceous species-coated ZnO rod arrays during 900 °C

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...