Nanofibers of asymmetrically substituted bisphenazine through organogelation and their acid sensing properties†
Abstract
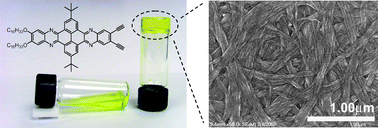
This paper reports the formation of an organogel of an asymmetric bisphenazine through the growth of one-dimensional nanofibers via a coopertive interplay of π–π interaction, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals interaction and the colorimetric acid sensing property of the nanofibers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...