Reversible hydrogen gas uptake in nanoporous Prussian Blue analogues†
Abstract
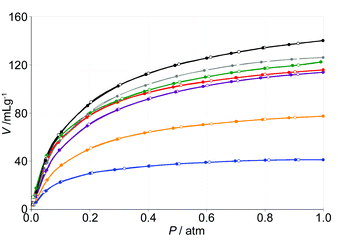
The family of dehydrated nanoporous Prussian Blue analogues, MII3[CoIII(CN)6]2 (MII = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd), which contain coordinatively unsaturated divalent metal cations, undergoes reversible sorption of hydrogen gas up to 1.2 wt% (at 77 K, 101.3 kPa), the capacity of which depends on the metal ion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...