RNA duplexes with biphenyl substituents as base replacements are less stable than DNA duplexes†
Abstract
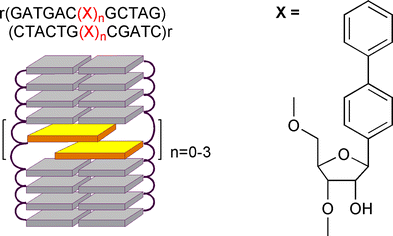
Introduction of a hydrophobic biphenyl-C-nucleotide pair into a 11-mer RNA duplex is associated with a net penalty in the free energy of duplex formation of 2.0 kcal mol−1 or 10 °C in Tm, relative to DNA. These differential stabilities are of relevance with respect to the transcriptional and translational aspects of hydrophobic base-pairs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...