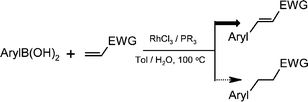
Rhodium-catalyzed Heck-type reaction of arylboronic acids with α,β-unsaturated esters: tuning β-hydrogen elimination vs.hydrolysis of alkylrhodium species
Abstract
The elusive rhodium-catalyzed Heck-type coupling of arylboronic acids with α,β-unsaturated

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...