Incorporation of a novel nucleobase allows stable oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation at the target sequence containing a purine·pyrimidine interruption†
Abstract
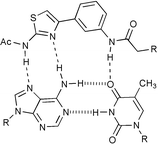
Thermal denaturation experiments have established that an
* Corresponding authors
a
Institut de Chimie des Substances Naturelles, CNRS, Avenue de la Terrasse, Gif-sur-Yvette Cédex, France
E-mail:
fourrey@icsn.cnrs-gif.fr
Fax: +33-1-69077247
Tel: +33-0169283053
b
Laboratoire de Biophysique, UMR 8646 CNRS-Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, INSERM U201, 43 rue Cuvier, Paris Cedex 05, France
E-mail:
sun@mnhn.fr
Fax: +33-1-69077247
Tel: +33-01407937
Thermal denaturation experiments have established that an

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Incorporation of a novel
D. Guianvarc'h, R. Benhida, J. Fourrey, R. Maurisse and J. Sun, Chem. Commun., 2001, 1814 DOI: 10.1039/B103743A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
