STAT3/IL-6 dependent induction of inflammatory response in osteoblast and osteoclast formation in nanoscale wear particle-induced aseptic prosthesis loosening†
Abstract
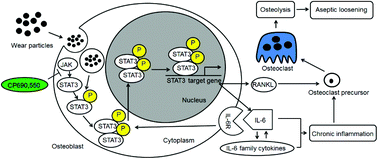
Background: Aseptic loosening is the main reason for surgical revision after arthroplasty. Although a series of mechanisms have been explored, a specific therapeutic target is still desired. In the present study, we explored the role of the signal transducer and activator of the transcription (STAT)/interleukin-6 (IL-6) pathway in the induction of the inflammatory response in osteoblast and osteoclast formation during aseptic prosthesis loosening. Methods: The expression of activated STAT3 was examined in osteoblasts treated with TiAl6V4 nanoparticles (TiPs) from materials used in prosthetics and specimens from particle-induced osteolysis (PIO) animal models. Inflammatory responses associated with the IL-6 family in osteoblasts were identified by Quantitative Real-time PCR. A mimicking coculture system was used to directly determine the number of activated osteoclasts in vitro, and immunohistochemical staining with tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) was used in vivo. CP690,550, an inhibitor of STAT3, was administered to examine the effect of STAT3 on the inflammatory response and osteoclast formation. Results: STAT3 was activated in both nanoparticle-treated osteoblasts and PIO model animals. On the one hand, the activation of STAT3 mediated nanoparticle-induced IL-6-dependent inflammatory responses in osteoblasts. On the other hand, the activation of STAT3 induced receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) production and stimulated osteoclast formation. The application of the STAT3 inhibitor CP690,550 reduced the production of the IL-6 family and the formation of osteoclasts both in vitro and in vivo. Conclusion: STAT3 mediated inflammation-related signalling and osteoclast activation in nanoscale wear particle-induced aseptic loosening. Inhibition of STAT3 by tofacitinib may be a potential treatment for aseptic loosening.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...