A study of microbially fabricated bio-conjugated quantum dots for pico-molar sensing of H2O2 and glucose†
Abstract
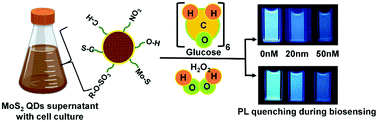
Quantum dots (QDs) as bio-detectors have been intensively explored owing to their size dependent optical properties and are still envisioned to be used in a plethora of biomedical and healthcare areas. However, the medical application of the biosensors demands the ultrasensitive detection of the analytes, which is usually limited for the conventional methods of colorimetric and fluorescence detection. The Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) process, exploited by QDs, translates the close association between the analyte and the detector into optical properties and thus promises the effective detection of biomolecules. FRET based detection systems for biomolecules utilize surface-functionalized QDs which are usually modified post production using different organic groups. In this work, a novel protocol was formulated to produce bio-functionalized QDs with controlled chemical and optical characteristics. Here, we demonstrate the first-ever biological green synthesis of MoS2 QDs using Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The bio-functionalized QDs show green luminescence with a quantum yield of 42%, supporting their application as an optical sensor. These QDs are utilized to detect the pico-molar concentration of glucose, which makes them ideal for early diabetes detection and many biomedical applications. Also, the ability to sense pico-molar levels of H2O2 opens the path for its utilization in apprehending the plant signaling pathways under stress conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...