“Dual-Key-and-Lock” dual drug carrier for dual mode imaging guided chemo-photothermal therapy†
Abstract
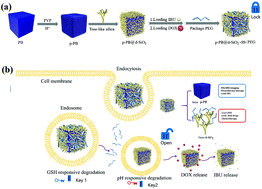
Drug resistance and side effects are the two main problems of chemotherapy. In order to address these big challenges, p-PB@d-SiO2, which has the ability to co-deliver both the hydrophobic drug doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) and the hydrophilic drug ibuprofen (IBU), is constructed to achieve synergistic treatment. The drug-loaded nanoparticle consists of porous Prussian blue (p-PB) as the core and dendrimer-like SiO2 (d-SiO2) as the shell, which is further thiolated and coated with polyethylene glycol thiol (HS-PEG) to form the “Dual-Key-and-Lock” drug carrier p-PB@d-SiO2-SS-PEG. The locked drugs can only be released in the presence of cooperative triggers, i.e., a high glutathione concentration (the first key) and an acidic environment (the second key). The “dual key”-triggered release is much more significant in cancer lesions than in normal tissues, reducing side effects. Furthermore, cell viability experiments highlight the superior therapeutic efficacy of the dual-drug-loaded nanoparticles compared with the single-drug systems (60%, 73% and 86% vs. 56%, 68%, and 76% at 100, 200 and 500 μg mL−1, respectively). In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrate the potential application of p-PB@d-SiO2-SS-PEG for dual-mode fluorescence and magnetic-resonance-imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy. The “Dual-Key-and-Lock” drug carrier system exhibits the “1 + 1 > 2” effect, demonstrating its excellent performance in synergy therapy for improved therapeutic efficiency and thereby reducing conventional drug resistance and side effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...