An acidity-responsive polyoxometalate with inflammatory retention for NIR-II photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic antibacterial therapy†
Abstract
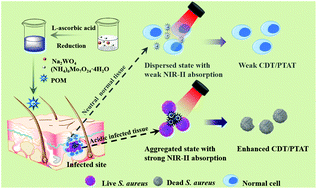
Subcutaneous abscesses caused by drug-resistant pathogens pose a serious challenge to human health. To overcome this problem, herein an acidity-responsive aggregated W/Mo-based polyoxometalate (POM) was developed for photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic antibacterial therapy in the second near-infrared (NIR) region. The POM can self-assemble into larger-sized aggregates with stronger absorption in the NIR region, making it remain in the acidic infected tissue. Furthermore, the hydrogen peroxide at the site of infection can be converted to a hydroxyl radical for chemodynamic therapy (CDT) and simultaneously the glutathione in organisms is consumed by the POM to further enhance the CDT effect. More importantly, under laser irradiation, the hyperthermia produced by the POM not only can kill drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, but also enhance the performance of CDT. Benefitting from the inflammatory retention and acidity-responsive photothermal-enhanced CDT properties, the POM exhibits an obvious therapeutic effect against drug-resistant bacterial infection without significant side effects under 1060 nm laser irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...