Attenuated Salmonella typhimurium-mediated tumour targeting imaging based on peptides†
Abstract
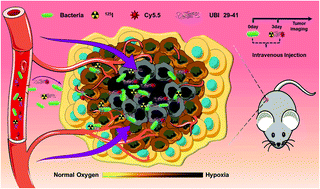
Attenuated bacteria-mediated tumor targeting diagnosis will provide a novel strategy for further cancer treatments owing to the intrinsic facultative anaerobic characteristic of bacteria and rapid proliferation in the tumor sites. In this work, we firstly investigate the in vivo behaviour of the attenuated Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium ΔppGpp/lux) after intravenous injection. S. typhimurium exhibits rapid proliferation in tumor sites after three days of injection through bioluminescence imaging, the Luria–Bertani plate and the Gram-staining assay. In contrast, S. typhimurium does not proliferate in the normal tissues and could be excreted from the body of mice. Afterwards, a targeting peptide ubiquicidin (UBI) labeled with fluorescent dye Cy5.5 or radionuclide 125I was intravenously injected into the mice with or without S. typhimurium treatments for in vivo fluorescence imaging and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT/CT) imaging, respectively. The results show that the peptide UBI could specifically target the two independent bacteria-infected tumor models, the 4T1 murine breast cancer model and the CT26 mouse colon cancer model, realizing the sensitive multimodal imaging of tumors. Such a strategy (bacteria-mediated tumor targeting) may further improve the sensitivity to early diagnosis of tumors. We hope that our developed strategy could further be extended to cancer theranostics in the future, bringing good news for cancer patients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...