Dose optimization of decellularized skeletal muscle extracellular matrix hydrogels for improving perfusion and subsequent validation in an aged hindlimb ischemia model
Abstract
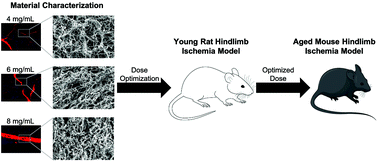
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) affects more than 27 million individuals in North America and Europe, and current treatment strategies mainly aim to restore blood perfusion. However, many patients are ineligible for existing procedures, and these therapies are often ineffective. Previous studies have demonstrated success of an injectable decellularized skeletal muscle extracellular matrix (ECM) hydrogel in a young rat hindlimb ischemia model of PAD, but further pre-clinical studies are necessary prior to clinical translation. In this study, varying concentrations of a skeletal muscle ECM hydrogel were investigated for material properties and in vivo effects on restoring blood perfusion. Rheological measurements indicated an increase in viscosity and mechanical strength with the higher concentrations of the ECM hydrogels. When injecting dye-labelled ECM hydrogels into a healthy rat, differences were also observed for the spreading and degradation rate of the various concentrations. The three concentrations for the ECM hydrogel were then further examined in a young rat hindlimb ischemia model. The efficacy of the optimal ECM hydrogel concentration was then further confirmed in an aged mouse hindlimb ischemia model. These results further validate the use of decellularized skeletal muscle ECM hydrogels for improving blood perfusion in small animal models of PAD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
