Enhanced selectivity, cellular uptake, and in vitro activity of an intrinsically fluorescent copper–tirapazamine nanocomplex for hypoxia targeted therapy in prostate cancer†
Abstract
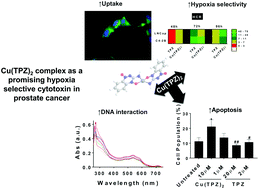
In the present work, a copper–tirapazamine (TPZ) nanocomplex [Cu(TPZ)2] was synthesized for selective hypoxia-targeted therapy. The nanocomplex revealed a crystalline form, and exhibited higher lipophilicity, compared to TPZ. Furthermore, its stability was confirmed in different media, with minimum dissociation in serum (∼20% up to 72 h). In contrast to other hypoxia-targeted agents, our intrinsically fluorescent nanocomplex offered an invaluable tool to monitor its cellular uptake and intracellular distribution under both normoxia and hypoxia. The conferred higher cellular uptake of the nanocomplex, especially under hypoxia, and its biocompatible reductive potential resulted in superior hypoxia selectivity in two prostate cancer (PC) cell lines. More promisingly, the nanocomplex showed higher potency in three-dimensional tumor spheroids, compared to TPZ, due to its slower metabolism, and probably deeper penetration in tumor spheroids. Interestingly, the nuclear localization of the intact nanocomplex, combined with its higher DNA binding affinity, as evidenced by the DNA binding assay, resulted in significant S-phase cell-cycle arrest, followed by apoptosis in the three-dimensional spheroid model. In conclusion, the presented findings suggested that the Cu(TPZ)2 nanocomplex can be a promising hypoxia-targeted therapeutic, which could potentiate the efficacy of the existing chemo- and radiotherapy in PC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...