A near infrared light-triggered human serum albumin drug delivery system with coordination bonding of indocyanine green and cisplatin for targeting photochemistry therapy against oral squamous cell cancer†
Abstract
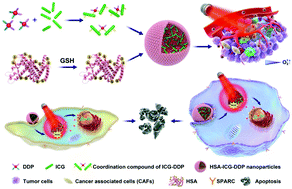
To ensure site–specific drug delivery/release in tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and reduce the systemic toxicity of chemotherapy, a novel drug delivery system called human serum albumin-indocyanine green-cisplatin nanoparticles (HSA-ICG-DDP NPs) was developed in our study. We characterized this system in vitro and in vivo and showed synergistic effects with photodynamic therapy (PDT), photothermal therapy (PTT) and chemotherapy; thereby it can significantly improve therapeutic efficacy compared with cancer monotherapy. High expression of secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) in oral squamous cell cancer (OSCC) and CAFs was also confirmed in our study. Our study also found that the cellular uptake of HSA-ICG-DDP NPs in tumor cells and CAFs can be enhanced by SPARC-mediated endocytosis. Cisplatin (DDP) release from the NPs in the tumor site can be precisely triggered by the cleavage of the coordination bond of ICG-DDP via a near infrared (NIR)-induced photothermal effect of ICG. Treatment with HSA-ICG-DDP NPs induced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cytotoxicity in SPARC-highly expressed tumor and CAFs. On in vivo treatment, HSA-ICG-DDP NPs were accumulated within the tumor tissue, where they exhibited stronger antitumor effects, compared to treatment with ICG, HSA-ICG and DDP. Therefore, this novel NIR-triggered drug release system displays potential for the improvement of OSCC treatment through its synergistic effects of PTT/PDT and chemotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...